Introduction: Unravelling the Intricacies of the Trigeminal Nerve
The trigeminal nerve is a critical component of the human nervous system, responsible for facilitating various sensory and motor functions within the face. Named after its three main branches, the trigeminal nerve plays a pivotal role in transmitting sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature from the face to the brain. While often overlooked, this complex nerve is a subject of increasing interest due to its involvement in various medical conditions, prompting the question: Is the trigeminal nerve serious?
Tapentadol 200mg is a larger dose of the medicine used to treat moderate to severe pain. Tapentadol 200mg, like the 100mg dosage, is an opioid analgesic. Its mode of action includes binding to the mu-opioid receptor and blocking norepinephrine reuptake, resulting in dual pain relief benefits.
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve
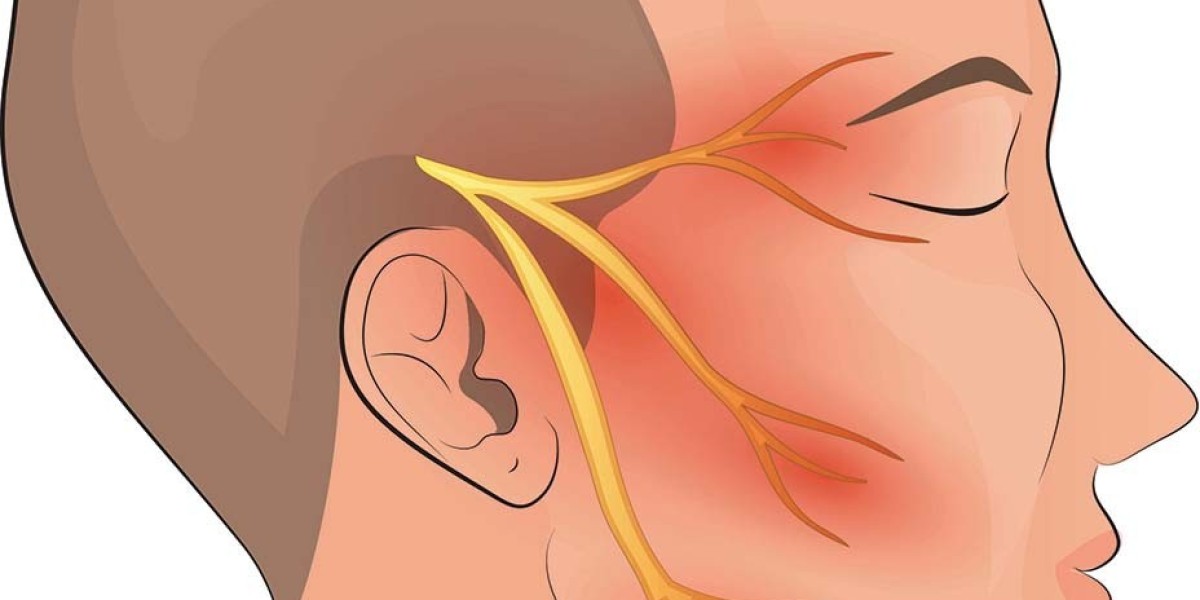
The trigeminal nerve consists of three main branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). Each branch serves a distinct region of the face, with the ophthalmic nerve innervating the forehead and eye, the maxillary nerve supplying sensation to the midface, and the mandibular nerve controlling the lower face and jaw.
Functionality of the Trigeminal Nerve
The trigeminal nerve performs both sensory and motor functions. Sensory fibres transmit information about touch, pain, and temperature from the face to the brain, allowing individuals to perceive and respond to external stimuli. Additionally, the trigeminal nerve plays a crucial role in motor functions such as chewing, biting, and swallowing, contributing to essential everyday activities.
Common Disorders of the Trigeminal Nerve
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a debilitating condition characterised by sudden, severe facial pain, often described as stabbing or electric shock-like sensations. This condition typically affects one side of the face and can be triggered by mundane activities such as eating, talking, or even touching the face lightly. While the exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia remains elusive, it is believed to stem from compression or irritation of the trigeminal nerve.
Tapentadol 100mg is a medicine used to relieve moderate to severe pain. It is an opioid analgesic. The major method of action is to bind to the mu-opioid receptor and impede norepinephrine reuptake. This multimodal mechanism helps manage pain by influencing both the opioid and noradrenergic pathways.
Trigeminal Neuropathy
Trigeminal neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the trigeminal nerve, leading to altered sensation or facial weakness. This condition can manifest as numbness, tingling, or a loss of sensation in the affected areas of the face. Trigeminal neuropathy may result from various causes, including trauma, infections, or underlying medical conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis
Diagnosing disorders of the trigeminal nerve often involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. In some cases, additional tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction tests, may be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes.
Treatment
The management of trigeminal nerve disorders depends on the underlying condition and the severity of symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Anticonvulsant medications such as carbamazepine or gabapentin may help alleviate pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia.
- Surgical Interventions: For individuals who do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical interventions such as microvascular decompression or nerve blocks may be considered to relieve pressure on the trigeminal nerve.
- Non-Invasive Therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, physical therapy, or nerve stimulation may provide relief for some patients with trigeminal nerve disorders.
Buy tapentadol online is a centrally acting analgesic (pain reliever) that treats moderate to severe pain. It is classed as an opioid analgesic and comes in both immediate and extended-release forms. Tapentadol binds to mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system and inhibits norepinephrine reuptake.
Conclusion: Addressing Concerns About the Trigeminal Nerve
In conclusion, the trigeminal nerve is a vital component of the human nervous system, playing a crucial role in sensory and motor functions within the face. While disorders of the trigeminal nerve can be debilitating, advances in medical understanding and treatment options offer hope for individuals affected by these conditions. By raising awareness and promoting further research, we can continue to unravel the complexities of the trigeminal nerve and improve outcomes for patients worldwide.